How to implement BlueArch Alerts Engine AMI
Running the CloudFormation Template in the Organization Manager (Root) Account
- Navigate to the AWS Console, search for CloudFormation, and click on it.
- Click the Create stack button.
- Choose Upload a template file and click Choose file.
- If you do not have Trusted Access with AWS Organizations to use service-managed permissions (Doc reference), this banner will appear:

- Select Activate trusted access. Trusted access is successfully activated when the following banner displays:

- Select the
manager-stackset.ymlfile and click Next. - Fill in the parameters mentioned in the next section and click Next.
- Click Next again.
- Check the box I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources and click Create stack.
- Wait for the stack to be created.
Running more than one instance of the application
- In case you want to scan a different Organization Unit or AWS Account, you can deploy a new stackset using different parameter values in the
Organization ID,AWS Account IDsandWorkspaceparameters.
CloudFormation Parameters
Organization Parameters
Organization ID*: Your Organization ID (ex r-1234, ou-abcd-12345). Either root organization id or OU ids. You can find it in the AWS Console, Organizations menu: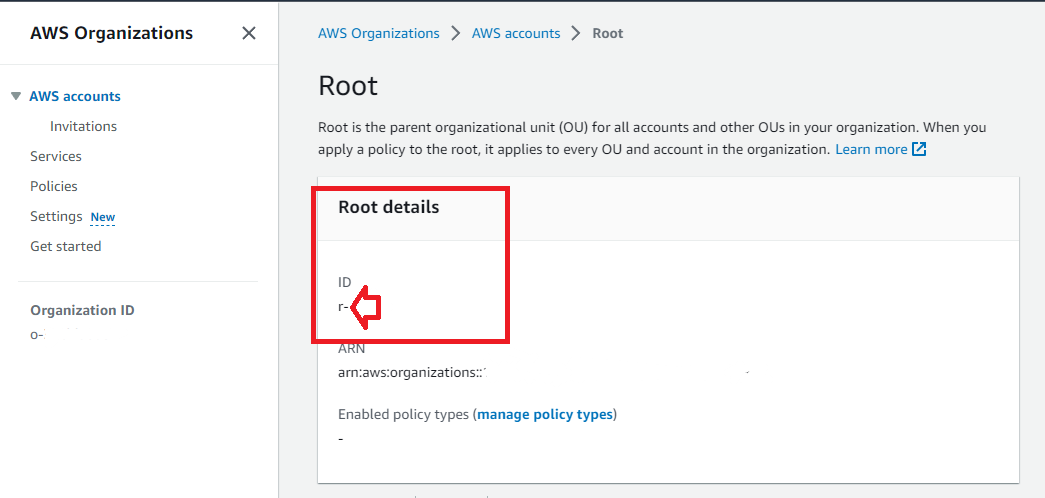
StackSets Deployment Region*: The region where the CloudFormation stacks will be deployed. It must be the same region where the CloudFormation template is being deployed (default = us-east-1).AWS Account IDs(optional): List of additional AWS Accounts to be scanned outside the selected organization IDs.VPC IP*: The CIDR block for theVPC(default = 10.10.0.0).
Amazon EC2 Configuration
Instance Type*: EC2 instance type to be used for the Alerts Engine Application (default = t3.medium).
Alerts Engine General Configuration
Workspace`* (must be unique)`: The name of the workspace to be created (Will be used in S3 paths).Email list*: List of email addresses to receive Excel report files (comma separated).
Detect Idle RDS Parameters
Days to query RDS DB Connections*: Number of days to query for RDS database connections (default = 7).
Detect Underutilized RDS Parameters
Days to query RDS CPU Utilization*: Number of days to query for RDS CPU utilization (default = 7).Days to query RDS Read IOPS*: Number of days to query for RDS read IOPS (default = 7).Days to query RDS Write IOPS*: Number of days to query for RDS write IOPS (default = 7).RDS CPU Utilization Threshold*: Threshold for RDS CPU utilization to be considered underutilized (default = 40).RDS Read IOPS Threshold*: Threshold for RDS read IOPS to be considered underutilized (default = 100).RDS Write IOPS Threshold*: Threshold for RDS write IOPS to be considered underutilized (default = 100).
Detect Idle Application Load Balancers Parameters
Days to query Application Load Balancer Request Count*: Number of days to query for ELBv2 request count (default = 7).Period in hours to validate the Request Count threshold*: Period in hours to query for ELBv2 request count (default = 6).Application Load Balancer Request Count Threshold*: Threshold for ELBv2 request count to be considered underutilized (default = 100).*= Required
Architectural Diagram
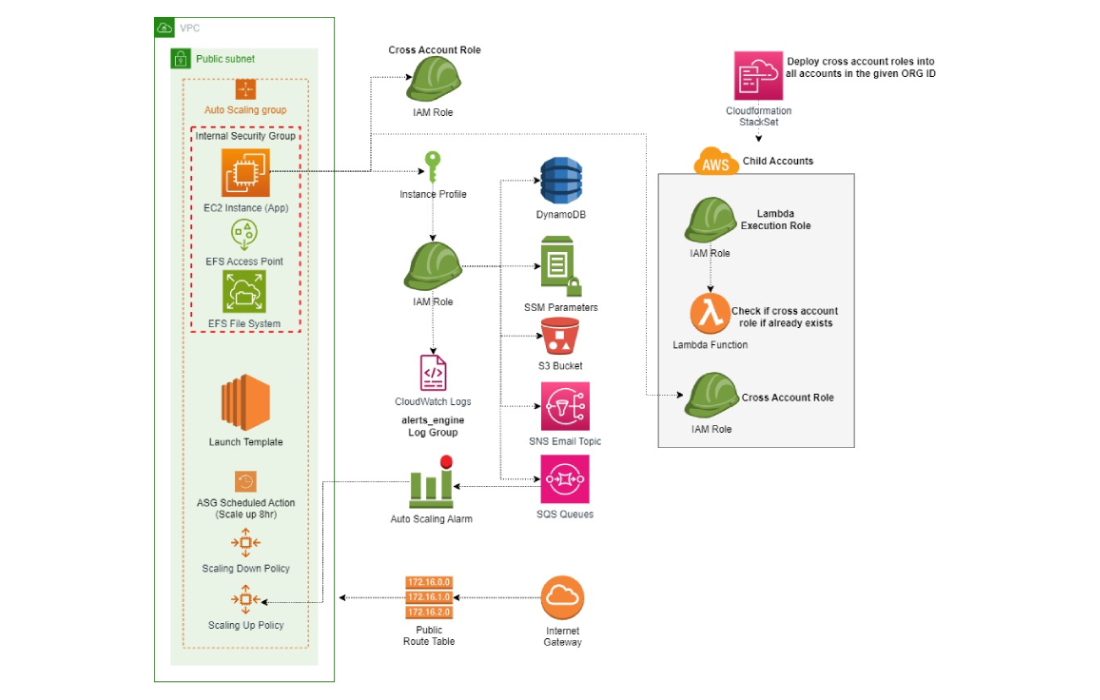
Resources Created by the CloudFormation StackSet
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
ExcelBucket |
The S3 Bucket where Alerts Engine will store its Excel report files. |
EC2Role |
IAM Role that allows the application to interact with the Alerts Engine resources inside the current account. |
EC2InstanceProfile |
Instance profile for EC2Role. |
EC2LaunchTemplate |
The launch template for the current AMI Product. |
EC2AutoScalingGroup |
AutoScalingGroup resource that will scale in and scale out the Alerts Engine Application. |
ScaleIn8h |
EC2AutoScalingGroup Scheduled Action (CRON) to scale the application in every day at 8 AM. |
EC2ScaleDownPolicy |
EC2AutoScalingGroup Scaling Down Policy - The application will trigger this policy when it finishes running, terminating the instances. |
SNSEmailTopic |
AWS SNS Topic - The application will send the excel report file through this topic every day to all emails inside the EMailList Parameter. |
CrossAccountAccessRoleForBlueArch |
IAM Role that allows the application to assume it and collect the necessary data for the application to work. |
Multiple SSM Parameters |
Refer to all parameters you filled in the CloudFormation Parameters section. |
BlueArchRoleStackSet |
CloudFormation Stackset that will deploy the CrossAccountAccessRoleForBlueArch in all accounts inside the organization. More information about StackSets. |
TaskTrackingDynamoDBTable |
DynamoDB table that will store the running instance IDs and its current tasks statuses. |
AccountsFIFOQueue |
SQS FIFO Queue that will store the AWS account ids that will be scanned by the application. |
SQSAutoScalingPolicy |
AutoScaling Policy that will scale out the EC2AutoScalingGroup based on the number of AWS account ids in the queue. |
SQSAutoScalingAlarm |
CloudWatch Alarm that will trigger the SQSAutoScalingPolicy based on the AWS account ids in the queue. |
EFS |
EFS File System that will store the application files. |
MountEFS |
EFS Mount Target that will be used by the EC2 instances to mount the EFS File System. |
Pricing
Click here to check the pricing estimations based on the Default values (typical deployment).
Starting the Application
Once you have created the CloudFormation StackSet in the Organization manager account, the application will start automatically via the EC2 AutoScaling Group.
Stopping the Application
It’s unnecessary to stop the application manually. It will stop automatically after it finishes running due to the EC2 AutoScaling Group scale-down policy.
How the Application Works
The application collects resources details and metrics from all accounts, stores them in the S3 bucket, processes the collected information, and sends alerts to the emails listed in the Email list parameter. Once the application finishes running, you are going to receive a temporary S3 Signed URL to download the Excel report file, in your email. All report files are also stored in the S3 bucket, and you can find their URLs in the Output CloudFormation tab. To check which AWS features are supported in the current version, check the Supported Resources section at the bottom of the page.
Customer Information Disclaimer
This product collects your name and email address. This information is sent to and stored by BlueArch. This information will only be used to contact the buyer in regards to the Alerting Engine.
How to remove everything
- Empty the S3 bucket created by the CloudFormation StackSet:
- Navigate to the AWS Console, search for S3, and click on it.
- Click on the
bluearchio-alerts-enginebucket. - Click on the Empty button.
- Type
permanently deletein the confirmation box and click Empty.
- Delete the Cloudformation Stack you created:
- Navigate to the AWS Console, search for CloudFormation, and click on it.
- Under Stack section, click on the BlueArch Alerts Engine you’ve created before.
- Click on the Delete button.
- Wait for the stack to be deleted.
Checking the Logs
- Open the AWS Console, search for CloudWatch, and click on it.
- Click on
Logs/Log groupson the left side menu. - Click the
alerts_enginelog group. - Check the latest log stream to see the logs.
Supported Resources in the Current Version (v1.3.1):
EC2 Instances
- Underutilized EC2 Instances
- Idle EC2 Instances
RDS
- Underutilized RDS Instances
- Idle RDS Instances
EBS
- Volumes to delete
- Volumes to encrypt
- Outdated Snapshots
IAM Roles
- Roles to delete (Inactive roles)
Application Load Balancer
- Idle Load Balancers